By Anu V. Pai, Commodity Research Analyst
As we are half way into 2020, the year has so far turned out be a highly turbulent one. While the global economy has been under duress of geopolitical and trade tensions, the rapid spread of Covid-19 pandemic came as a jolt, which saw a meltdown across the financial and commodity markets. The outbreak of this pandemic in China and later, a swift spread to other countries have stalled socio-economic activities, affecting livelihood, creating demand-supply imbalances and unsettling supply chains. Commodity prices, especially crude oil and industrial metals came tumbling down and among the agriculture commodities natural rubber was one of the most afflicted.
Natural rubber has been grappling with the bearish market forces for a long time now, the circumstances that emerged due to pandemic have deepened the crisis. It has given rise to an unprecedented situation with both demand and supply sides being impacted simultaneously. The spread of new Pestalotiopsis fungal disease in plantations of Indonesia, Thailand and Malaysia along with subdued prices and unfavorable weather had led to a marginal decline in global natural rubber production last year and now the pandemic is posing a threat of a greater decline in output. The Association of Natural Rubber Producing Countries (ANRPC) in its April release of Natural Rubber Trend and Statistics revised down its outlook on world production and consumption in the backdrop of Covid-19 pandemic. The organization now expects world natural rubber production in 2020 to be at 13.433 million tonnes, a downfall of 2.3 per cent from the previous year and a decline of 679000 tonnes in from the forecast of 14.112 million made during March this year. According to Jom Jacob, Senior Economist at the ANRPC, the global natural rubber production contracted by 3.6 per cent in the first quarter of this year. Barring India, most of the other major natural rubber producing countries registered a negative growth and for the first half of this year a decline by more than six percent is expected in global natural rubber production. While it has been lean production phase in some of the key natural rubber production countries during February to March-April period, various restrictions being placed for containing the spread of the pandemic like social distancing, restrictions on transport etc. made it difficult for production and other allied activities to resume or continue. The steep decline in natural rubber prices coupled with a sudden drop in demand following halt in industrial activities also dissuaded the farmers to actively tap and take up other production related activities.
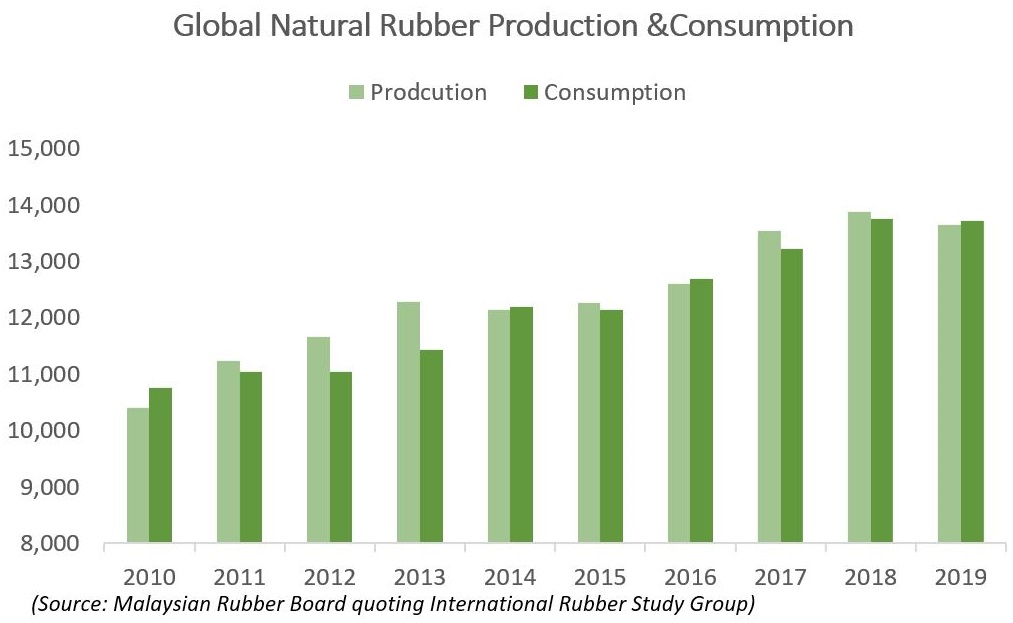
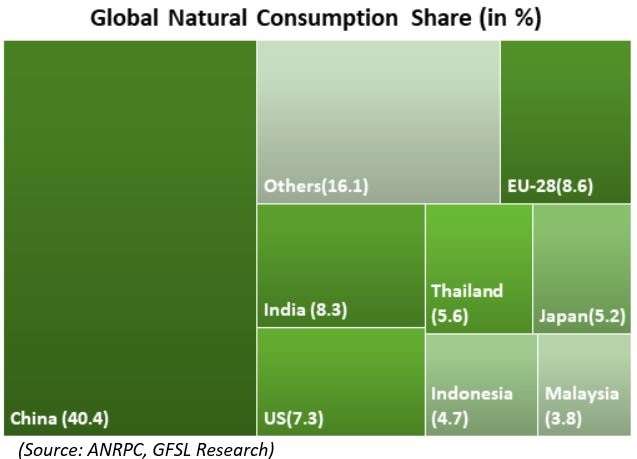
In the meantime, the fall in consumption is anticipated to be much higher compared to production. The International Monetary Fund expecting a contraction in economic growth in 2020 and fall in demand from the auto-sector, which consumes over 75 per cent of the total natural rubber output, being hit due to the implementation of various measures to contain the spread of the pandemic could hamper consumption. Moreover, the countries that are severely affected by the coronavirus are the major consumers of natural rubber and some of the main auto-markets in the world. China, EU-28 and the US were severely affected due to the virus and there has been a surge in number of cases in India and these countries together constitute nearly 65 per cent of total consumption.
The ANRPC estimate shows the global off-take of natural rubber plunged by a whopping 20 per cent in the first quarter of 2020 and expects 16 per cent fall in first half, a 5.1 per cent annualized fall in consumption this year to 13.016 million tones, a shortfall of 516000 tones in relation to the forecast made a month ago. In the meantime, there were some green shoots as well. There was a surge in demand for rubber gloves and other rubber based health care products as the pandemic began to spread rapidly. The Association estimates that Covid-19 may generate additional demand for natural rubber in the tune of 150000 tonnes in 2020. Yet, it may help only partially to offset the loss due to fall in demand from the tire sector.
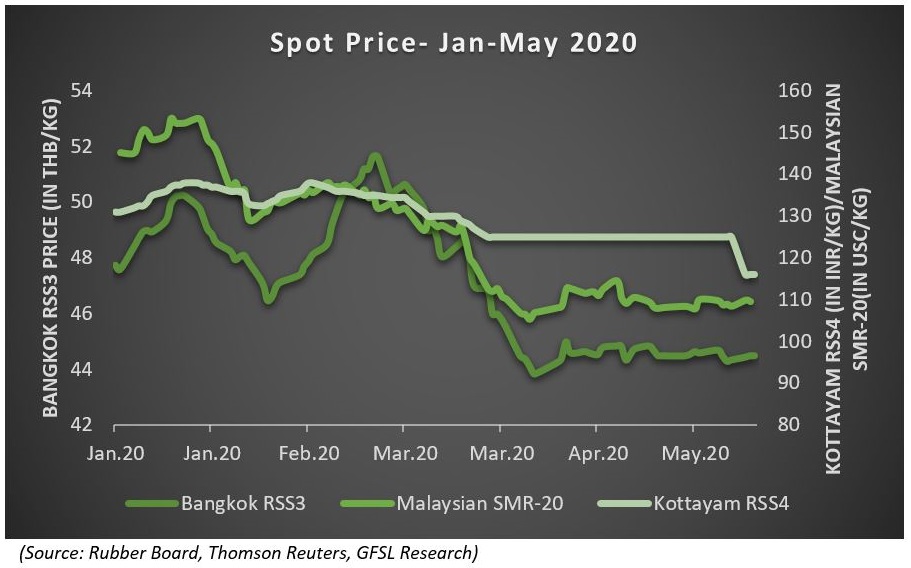
Currently, natural rubber prices on the major overseas exchanges like Tokyo Commodity Exchange and Shanghai Futures Exchange are down by over 20 per cent so far this year, while in the Indian market it has shed more than 10 per cent.
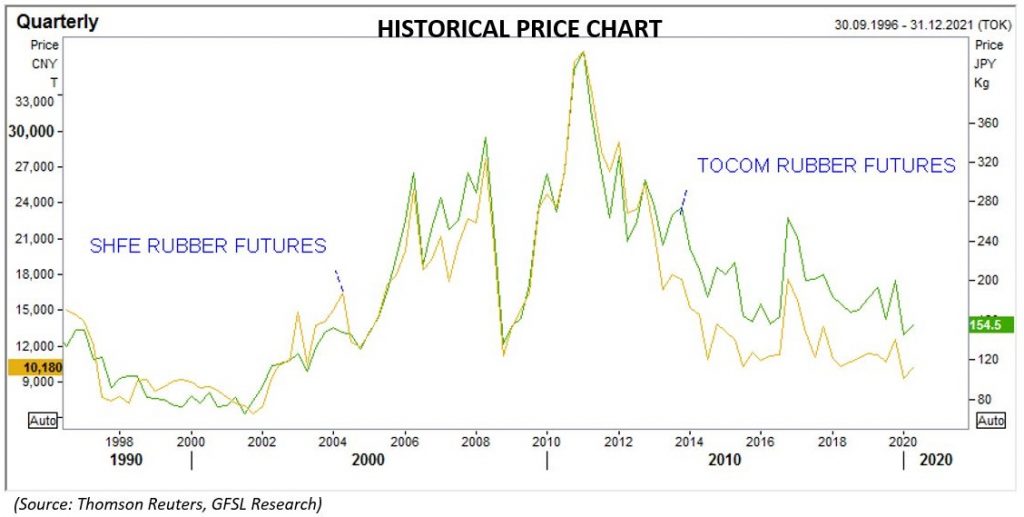
The commodity was trading relatively on a firmer note in the beginning of 2020. Easing geopolitical tensions in the Middle-East and prospects of the US-China trade deal improved sentiments amidst spread of new Pestalotiopsis fungal disease, affecting many plantations in the major rubber growing belt of South-East Asia, which affected production. However, there was dramatic shift in the situation with the reports of spread of a flu-like virus in China, the second largest economy and the major consumer of many commodities including natural rubber. The various restrictions imposed by China to curb the spread of coronavirus resulted in disruptions in industrial activity and demand for rubber. Natural rubber consumption by China, which accounts for about 40 per cent of the global total, slumped by 34 per cent in the first quarter of this year according to the ANRPC. Later, a brief bounce in natural rubber prices witnessed in February was short-lived with virus beginning to spread rapidly far outside China. With many countries going for lockdowns, imposing travel and transport restrictions and other measures to curb the spread of the pandemic, the economic activity across the globe was severely impacted. As a good chunk of demand for natural rubber comes from auto sector, shutdown of many automobile and tire manufacturing units intensified the downward momentum in prices.
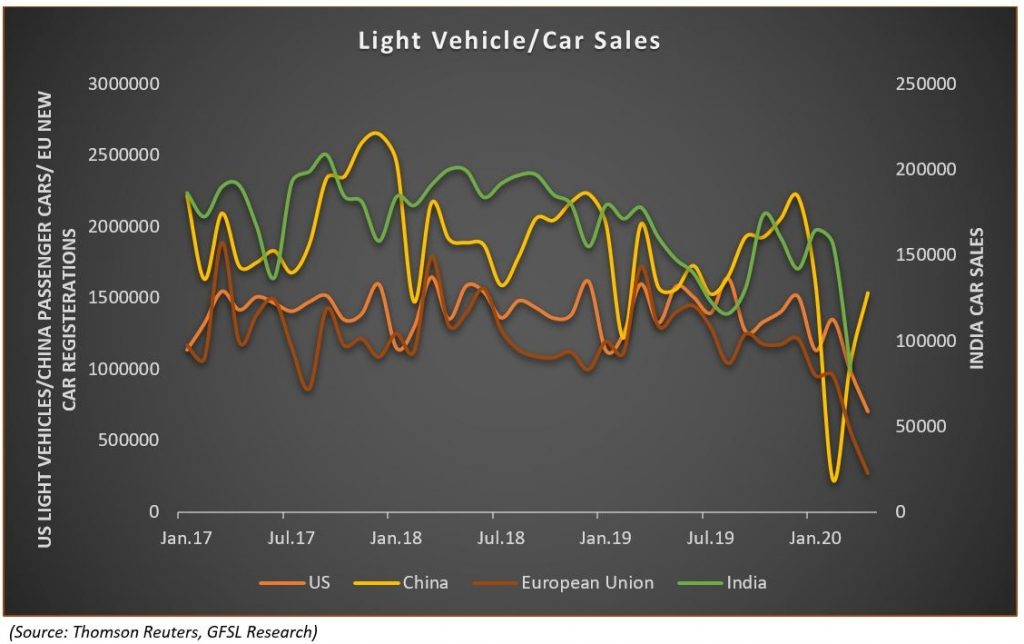
Apart from the demand disruptions for the auto sector, the steep fall witnessed in crude oil in April following the fallout of output cut agreement between the OPEC+ countries as well as due to an unprecedented drop in oil demand following restrictions on transport to contain the spread of virus fanned the downfall in natural rubber prices. Crude oil prices tumbled with WTI on NYMEX charting new historical lows in April before bouncing back. Subsequently, natural rubber prices in the TOCOM exchange fell to its lowest level since 2009 in April and on SHFE, it was quoted at its weakest level since 2002. In the Indian market, the commodity in the futures market had hit multi-year lows in tandem with global markets, and is trading down 15 per cent so far this year. Meanwhile, the key spot markets in Kerala that were closed following the nation-wide lockdown announced on March 23 have reopened and RSS4 grade rubber is hovering near its lowest level since Nov-2016.
The outlook for natural rubber seems to be not so promising with high amount of uncertainty lingering in the market in the backdrop of Covid-19 pandemic. By and large, the developments with regards to the spread and containment of the virus could influence the market sentiments in the near future. While China was already out of containment measures by March, when the number of cases started to recede in the country, many key natural rubber producing and consuming countries like the US, India, Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia have started to ease the lockdown measures recently, which is an upbeat signal. However, an immediate revival in demand could be least anticipated. Many auto-tyre manufacturing and other rubber goods manufacturing units have resumed operations in China, US, EU-28, India, Malaysia, Thailand etc. but only partially with hindrances being faced due to slump in demand, supply chain disruptions and possible postponement of purchases owing to financial constraints. Looking forward, the factors that can predominantly dictate the price trend in the near futures are:
- Covid-19 Pandemic- spread, intensity and containment
- Stimulus packages to reinvigorate the economic activity and global economic recovery
- Demand from China
- Auto sector demand
- Demand from the rubber goods manufacturing sector
- Consumer confidence
- Trend in crude oil prices
- Response of farmers to fluctuation in natural rubber prices (by increasing/decreasing production).
- Weather and climatic conditions
Apart from the above mentioned factors, attempts by the key natural rubber producing countries to raise the output and consumption through various schemes and other market intervention measures could influence the sentiments as well.








